If for a Firm P Minimum Atc Mc Then
Neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being achieved b. Allocative efficiency is being achieved but productive efficiency is not.

Pin On Intermediate Microeconomics
Productive efficiency is being achieved but allocative efficiency is not.
. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then Aneither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being achieved. Allocative efficiency is being achieved but productive efficiency is not.
If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then. Dallocative efficiency is being achieved but productive efficiency is not.
B allocative efficiency is being achieved but productive efficiency is not C neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being D productive efficiency is being. B Productive Efficiency Is Being Achieved But Allocative Efficiency Is Not C Both Allocative Efficiency And Productive Efficiency Are Being Achieved. Neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being achieved.
Productive efficiency is being achieved but allocative efficiency is not. A Neither Allocative Efficiency Nor Productive Efficiency Is Being Achieved. When a firm sets its price on the basis of the price being charged.
Fulfilling the condition P MC. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then a. Both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved.
Economics questions and answers. Productive efficiency is being achieved but allocative efficiency is not. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then.
Both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved d. A perfectly competitive firm is precluded from making economic profit in the long run because. Productive efficiency is being achieved but allocative efficiency is not.
In long-run equilibrium purely competitive markets. Allocative efficiency is being achieved but productive efficiency is not. This specific point happens when Demand is tangent to ATC because only when this is true can P ATC given that ATC is downward sloping recall that the MC curve passes through ATC at the minimum point of ATC and note that the minimum point of ATC is at a quantity higher than that produced by the.
As shown in Figure 84d this occurs when P ATC and MR MC. The MRMC rule can be restated for a purely competitive seller as PMC because each additional unit of output adds exactly its price to total revenue A purely competitive firms short run supply curve is up sloping and equal to portion of marginal cost curve that lies above average variable cost curve Suppose you find that the price of your product is less than the minimum. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then.
Neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being achieved. If For A Firm P Minimum ATC MC Then. Both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved.
Both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved. The Woes of T-Shirt Shops states that if T-shirt shops are perfectly competitive firms then each shop A Is a price setter. Cboth allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved.
Both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then A. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then.
Productive efficiency is being achieved but allocative efficiency is not. Both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved. C it produces a differentiated product.
Bproductive efficiency is being achieved but allocative efficiency is not. The MR curve is. Monopolist Look at the scenario Monopolist.
Cboth allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved. Allocative efficiency is being achieved but productive efficiency is not. Neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being achieved.
70 A firm should shut down production when A P minimum ATC P minimum AVC C P MC from ECO 213 at Trine University. Assume also that ATC at the profit-maximizing level of production is equal to 1250. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then.
The point where MC crosses AC is called the zero-profit point. Both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved. Productive efficiency is being achieved but allocative efficiency is not.
Which of the following conditions is true for a purely competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. If for a firm P minimum ATC MC then. A it is a price taker B its demand curve is perfectly elastic.
If the firm is operating at a level of output where the market price is at a level higher than the zero-profit point then price will be greater than average cost and the firm is earning profits. 10 If for a firm P-minimum ATC MC then 0 A both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved. Neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being achieved.
The demand curve for a monopolist is P 75 - 05Q and the monopolist has the following MC expressed as P 2Q. Productive efficiency is being achieved but allocative efficiency is not c. Neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being achieved.
See Page 1. Both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are being achieved. If the price is exactly at the zero-profit point then the firm is making zero profits.
Entrepreneurs in purely competitive industries. Neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency is being achieved. P MC minimum ATC.

Solved 10 If For A Firm P Minimum Atc Mc Then 0 A Both Chegg Com
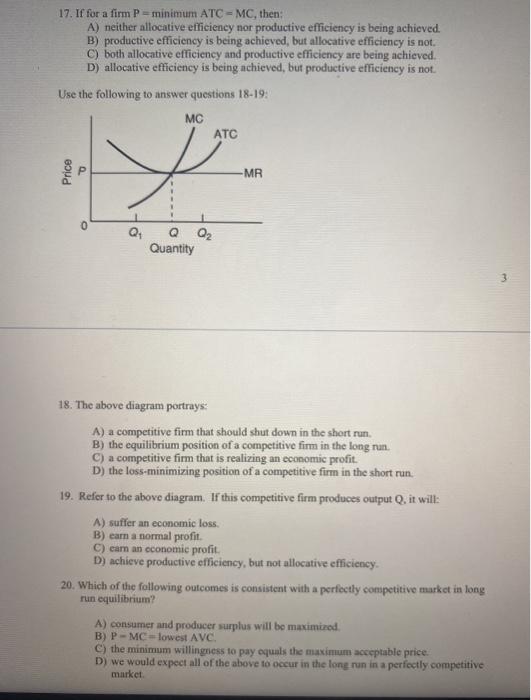
Solved 17 If For A Firm P Minimum Atc Mc Then A Chegg Com

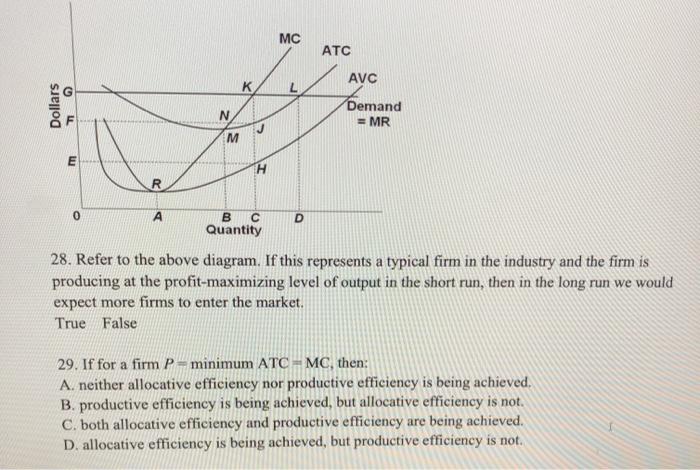
Solved Mc Atc Avc G Dollars N Demand Mr M E H R 0 A D B S Chegg Com
No comments for "If for a Firm P Minimum Atc Mc Then"
Post a Comment